search for package
You may encounter such a situation that some shared libraries are stripped when you debug core file. For example,
(gdb) info shared
From To Syms Read Shared Object Library
0xb778f430 0xb77a6054 Yes (*) /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libncurses.so.5
0xb75ef350 0xb7728f4e Yes /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
0xb75d2ad0 0xb75d3a9c Yes /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libdl.so.2
0xb75b87d0 0xb75c2c24 Yes (*) /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libtinfo.so.5
0xb77c9830 0xb77e1e7c Yes /lib/ld-linux.so.2
(*): Shared library is missing debugging information.
You would like to search for package, which relevant shared object is included. With library, which contains symbol table and you can examine more closely core file.
install
You need to have apt-file command for searching packages. Let’s install apt-file, as it is not installed by default.
$ sudo apt-get install apt-file
update cache
So as to search for packages, you need to have local cache. Let’s download cache from repository and update cache.
$ apt-file update
search & install
Now you are ready for searching packages. Take sample quoted above and search for “libncurses.so.5”.
$ apt-file search libncurses.so.5
lib64ncurses5: /lib64/libncurses.so.5
lib64ncurses5: /lib64/libncurses.so.5.9
libncurses5: /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libncurses.so.5
libncurses5: /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libncurses.so.5.9
libncurses5-dbg: /usr/lib/debug/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libncurses.so.5.9
libncurses5-dbg: /usr/lib/debug/lib64/libncurses.so.5.9
libncurses5-dbg: /usr/lib/debug/libncurses.so.5
libncurses5-dbg: /usr/lib/debug/libncurses.so.5.9
libncurses5-dbg: /usr/lib/debug/usr/libx32/libncurses.so.5.9
libx32ncurses5: /usr/libx32/libncurses.so.5
libx32ncurses5: /usr/libx32/libncurses.so.5.9
libncurses5-dbg must be our target package. Ok, let’s install it.
$ sudo apt-get install libncurses5-dbg
Now you can see stacks with function names and arguments. And checking status of shared libraries, you will confirm libraries not stripped.
(gdb) info shared
From To Syms Read Shared Object Library
0xb778f430 0xb77a6054 Yes /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libncurses.so.5
0xb75ef350 0xb7728f4e Yes /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
0xb75d2ad0 0xb75d3a9c Yes /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libdl.so.2
0xb75b87d0 0xb75c2c24 Yes /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libtinfo.so.5
0xb77c9830 0xb77e1e7c Yes /lib/ld-linux.so.2
resize disk size of guest on KVM
Sometimes you regret that you created guest OS with too small disk space. sigh... And you would like to increase disk space a little.
You can do it with some steps and I hereby quote a sample procedure of such operation. In this sample, OS of guest instance is Windows 7.
shutdown
Shutdown guest OS before start operation.
resize image file
Guest OS’s file system is represented in image file (*.img), which reflect its size.
$ du -sh /var/lib/libvirt/images/win7.img
21G /var/lib/libvirt/images/win7.img
Let us manipulate image file by qemu-img command. In this sample, 20GB will be added to existing file.
$ sudo qemu-img resize /var/lib/libvirt/images/win7.img +20G
Image resized.
resize partition
Now you need to resize existing partition to grow as much as you increased. For that sake, let us make use of gnome partition editor (gparted).
Download ISO file of gparted and connect it to guest instance. And boot from gparted. You will select graphical user interface of gparted and increase partition size easily.
boot
Now you can boot with guest OS and see that disk size does increase.
plotting
Sometimes you would like to create a plot out of some text file. You can achieve it by making use of matplotlib.
I have to confess that I am not quite accustomed with matplotlib though, I hereby demonstrate a sample.
installation
Installation is quite simple and one line command suffices.
$ sudo apt-get install python-matplotlib
sample
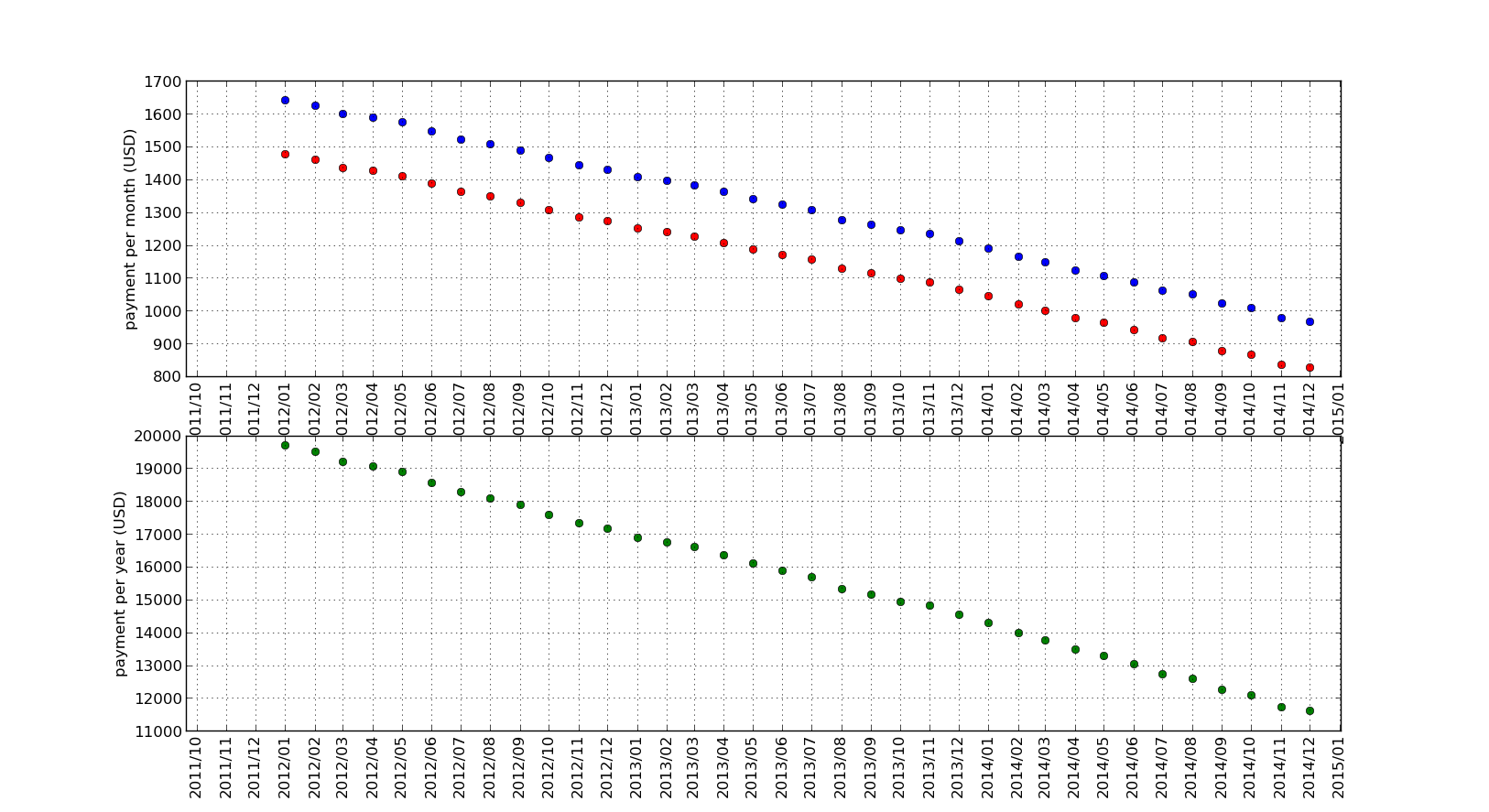
Suppose such a CSV file as follows.
201201,1477,994
201202,1462,988
201203,1437,985
That is, CSV file contains residential loan prepayment history. lines are consisted of,
- month of prepayment
- monthly payment
- bonus payment
plot
You can plot a graph, for example, as follows.
import csv
from datetime import datetime
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import dates
if __name__ == "__main__":
raw_data = "sample.csv"
fmt = ["prepay", "month", "bonus"]
# prepayment date
prepay = []
# lists to store each values
monthCal = []
monthAct = []
year = []
with open(raw_data, "rb") as f:
reader = csv.reader(f)
for row in reader:
prepay.append(dates.date2num(datetime.strptime(row[fmt.index("prepay")], "%Y%m")))
monthCal.append(int(row[fmt.index("month")]) + int(row[fmt.index("bonus")])/6)
monthAct.append(int(row[fmt.index("month")]))
year.append(int(row[fmt.index("month")])*12 + int(row[fmt.index("bonus")])*2)
# let's start plotting
fig = plt.figure()
# monthly graph
graph = fig.add_subplot(2, 1, 1)
graph.plot(prepay, monthCal, "bo", prepay, monthAct, "ro")
graph.xaxis.set_major_locator(dates.MonthLocator())
graph.xaxis.set_major_formatter(dates.DateFormatter("%Y/%m"))
plt.xticks(rotation="vertical")
plt.ylabel("payment per month (USD)")
plt.grid(True)
# yearly graph
graph = fig.add_subplot(2, 1, 2)
graph.plot(prepay, year, "go")
graph.xaxis.set_major_locator(dates.MonthLocator())
graph.xaxis.set_major_formatter(dates.DateFormatter("%Y/%m"))
plt.ylabel("payment per year (USD)")
plt.xticks(rotation="vertical")
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
fig.savefig(raw_data.replace("csv", "png"))